Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative(SSI)
About Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative
-
The major principles that govern SSI can be stated as below
-
Cultivation aspects
-
Fertigation schedule for sugarcane in SSI
-
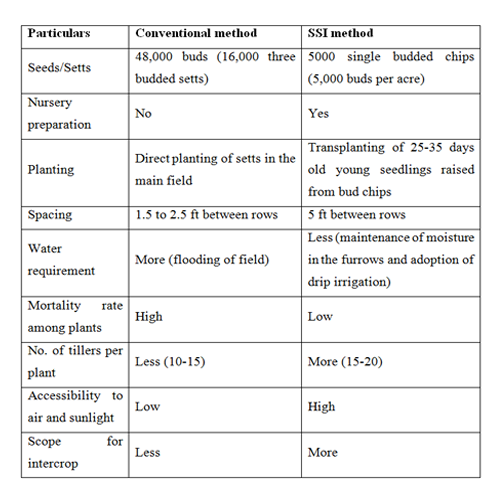
Comparison between Conventional and SSI methods of Sugarcane Cultivation
Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative
The major principles that govern SSI can be stated as below
Cultivation aspects
Fertigation schedule for sugarcane in SSI
Comparison between Conventional and SSI methods of Sugarcane Cultivation
|
 |
The major principles that govern SSI can be stated as below:
|
Cultivation aspects
Bud selection
|
 |
Nursery preparation
|
 |
Main field preparation
The main field preparation in SSI method is similar to that of conventional method. A good land preparation should be done. |
Fertilizer application
Nutrient management in sugarcane cultivation is very essential for crop growth. It is always better to know the required quantity of nutrients through soil testing and enrich the soil accordingly. If there is no facility for that, then NPK can be applied at the rate of 112 kg, 25 kg and 48 kg per acre, respectively through inorganic or organic methods. |
Transplanting
|
 |
Intercropping
SSI supports intercropping in sugarcane with crops like wheat, potato, cowpea, french bean, chickpea, water melon, brinjal etc. In addition to effective utilization of land, this practice will reduce the weed growth up to 60% and give extra income to farmers. |
Weeding
A weed-free environment is absolutely essential for efficient intake of nutrients. This can be achieved by: |
Mulching
Trash mulching is important in sugarcane cultivation as it helps in checking the weeds and providing needed moisture. Sugarcane trash can be applied @ 1.5 t/acre within 3days of planting. Similarly, after detrashing the removed leaves can be applied in the interspaces as mulch. |
Organic method of cultivation
The SSI method encourages application of organic manure as it enhances the macro and micro nutrient content in the soil in an eco friendly way, helps in optimum utilization of some of the chemical fertilizers and protects the soil from degradation and other hazardous effects.
|
 |
Water management
|
 |
Comparison between Flood irrigation and Drip fertigation in SSI
Particulars |
Flood Irrigation |
Drip Fertigation |
Water Requirement |
2200m.m |
1000m.m |
Duration of irrigation |
250 days |
250 days |
Irrigation Interval |
7 days |
1 day |
Number of irrigation |
36 |
250 |
Water requirement of single irrigation(lit) |
6.1 lakhs |
0.4 lakhs |
Yield |
92-105 t/ha |
150-200 t/ha |
Fertilizer Use Effieciency |
30% |
60% |
Benifit Cost Ratio |
1.97 |
4.7 |
Earthing up
|
Fertigation schedule for sugarcane in SSI:
RDF - 275:63:115 NPK kg/ha Once in 10 days
Stage (Day After Planting) |
(kg/ha) |
||
N |
P |
K |
|
0-30 |
39.4 |
0 |
0 |
31-60 |
48.6 |
26.25 |
9 |
61-90 |
51.4 |
20.50 |
13.5 |
91-120 |
55.2 |
16.25 |
14.6 |
121-180 |
57.8 |
0 |
40.5 |
181-210 |
10.5 |
0 |
35.0 |
Total |
275.0 |
63.0 |
115.0 |
Comparison between Conventional and SSI methods of Sugarcane Cultivation
Harvesting
Harvesting in sugarcane is practiced in collaboration with the industry, in most of the cases, to suit the factory timings. Sucrose content in the plants will reach the desirable level on the 10th month of the one year crop duration, and they will be ready for harvest within the next two months.
Overall benefits
• In conventional method, cost of setts occupies the major part of cost of cultivation
• By practicing SSI, this seed cost can be reduced up to 75%
• Reduction in the plant mortality rate
• Increases in the length and weight of each cane
• It is easy to transport the young seedlings for longer distance
• Intercultural operations can be carried out easily due to wider spacing
Scope of SSI in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu, being the number one state in sugarcane productivity (more than 100 t/ha), has a great potential in SSI. The following are some of the reasons to foresee the great impact of SSI in Tamil Nadu sugarcane sector.
-
Farmers are very much innovative, eager to take up any new technologies with great enthusiasm and support.
-
SSI will be a suitable option to solve the present problems of increasing seed cost, labour cost and other soil fertility and productivity related issues.
-
Due to wider spacing, intercultural operation becomes easy, thus reducing the drudgery among women labourers.
-
The wider spacing suggested in SSI are ideal in case of introducing Mechanical harvester, an effort already in practice in some of the Mills areas in Tamil Nadu.
Conclusion
SSI involves use of less seeds, less water and optimum land utilization to achieve more yields. It is governed by some principles like using single budded chips, raising nursery, wider spacing, sufficient irrigation and intercropping. By practicing these measures, the following benefits can be realized:
-
Better germination percentage
-
High number of millable canes
-
Reduction in the duration of crop to some extent
-
Increased water use efficiency
-
Improvement in accessibility to nutrients with optimum use of fertilizers
-
More accessibility to air and sunlight
-
Reduction in cost of cultivation and
-
Extra income from intercrops
On the whole, by practicing SSI farmers can very well increase their productivity by reducing the use of inputs like fertilizers and saving the vital resources like water simultaneously. Hence, it is very much possible for sugarcane farmers to reap greater economical benefits by maintaining ecological sustainability.

