|
Leaf scald
(Microdochium Oryzae)
| Symptoms |
|
| |
|
- Zonate lesions of alternating light tan and dark brown starting from leaf tips or edges
- Lesions oblong with light brown halos in mature leaves
- Coalescing of lesions result in blighting of a large part of the leaf blade
- The affected areas dry out giving the leaf a scalded appearance
- Translucent leaf tips and margins
- Infected leaf tips also split near the midrib especially when there are strong wind.
|
 |
 |
| Rice Leaf Scald Disease |
Leaf Scald |
|
| Top |
| |
Identification of pathogen |
|
|
 |
 |
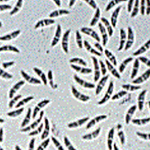
- The conidia are borne on superficial stromata (compact masses of specialized vegetative hyphae) arising from lesions.
- They are bow to new-moon shaped, single-celled when young and 2-celled when mature, occasionally 2-3 septate.
- Asci are cylindrical to club-shaped and unitunicate (an ascus wherein both the inner and outer walls are more or less rigid and do not separate during spore ejection).
- The ascospores are fusoid (tapering towards each end), straight or somewhat curved, 3-5 septate.
|
| Conidia of Rice
Leaf Scald
Pathogen |
Rice Leaf Scald Pathogen |
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies |
|
|
|
- Avoid high use of fertilizer.
- Chemicals such as benomyl, carbendazim, quitozene, and thiophanate-methyl can be used to treat the seeds to eliminate the disease.
- In the field, spraying of benomyl, fentin acetate, edifenphos, and validamycin significantly reduce the incidence of leaf scald.
- Foliar application of captafol, mancozeb, and copper oxychloride also reduces the incidence and severity of the fungal disease.
|
 |
 |
| Mancozeb |
Validamycin |
| Top |
|






