|
Bacterial leaf streak
(Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzicola)
| Symptoms |
|
| |
|
- Initially, small, dark-green and water-soaked streaks on interveins from tillering to booting stage
- The progress of the streaks is longitudinal, limited by the veins and soon turn yellow or orange brown.
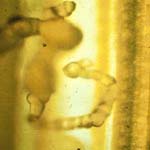
- All along the streaks bacterial exudates could be observed as tiny yellow or amber colored droplets.
- These streaks may coalesce to form large patches and cover the entire leaf surface.
- Lesions turn brown to greyish white then dry when disease is severe
- Infection in the florets and seeds results in brown or black discoloration and death of ovary, stamens and endosperm and browning of glumes.
|
 |
 |
Brown to Greyish
Longitudinal Streaks on
Leaves |
Lesions turn brown to greyish and drying of leaves |
|
| Top |
| |
Identification of pathogen |
|
|
 |
 |
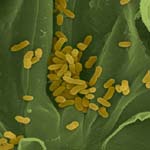
- The bacteria causing the disease X. oryzae pv.oryzicola occur as rods.
- The bacteria have no spores and no capsules.
- They move with the aid of a single polar flagellum.
- They are Gram-negative and aerobic and can grow favorably at 28 °C.
- The bacterial colonies on nutrient agar are pale yellow, circular, smooth, convex, and viscid and have an entire margin.
Factors favoring disease development
- Presence of the bacteria on leaves and in the water or those surviving in the debris left after harvest
- Warm temperature and high humidity
- Early stage of planting from maximum tillering to panicle initiation
|
Cells of Xanthomonas
Oryzae pv |
Exudate of Xanthomonas
Campestris pv. Oryzicola |
|
|
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies |
|
|
|
- The disease can be controlled by proper application of fertilizers and proper plant spacing, use of resistant varieties, and hot water treated seeds.
- Practicing field sanitation is important.
- Ratoons, straws and volunteer seedlings left after harvest can be destroyed to minimize the initial inoculum at the beginning of the season.
- Providing good drainage system especially in seedbeds can also manage this disease.
- Planting of resistant varieties (IR 20, TKM 6) is the most effective method of controlling bacterial leaf streak.
- Grow nurseries preferably in isolated upland conditions
- Avoid clipping of seedlings during transplanting.
- Spray fresh cowdung water extract or lemon grass or mint extract at 20 %.
- Spraying streptomycin sulphate and tetracycline combination 300g +copper oxychloride 1.25 kg/ha.
|
 |
 |
| Practice Field Sanitation |
Resistant Variety- IR 20 |
 |
 |
Spray Cowdung or Mint or
Lemongrass Extract |
Spray Streptomycin
Sulphate + Tetracycline |
| Top |
|








