|
Brown plant hopper
| Identification of pest : |
|
Scientific Name - Nilaparvata lugens
- Egg :
Eggs are laid in a group of 2 to 12 in leaf sheath (near the plant base or in the ventral midribs of leaf blades). White, transparent, slender cylindrical and curved eggs are thrust in straight-line in two rows. (They are covered with a dome - shaped egg plug secreted by the female. Only the tips protrude from the plant surface).
- Nymph :
Freshly hatched nymph is cottony white, 0.6 mm long and it turns purple-brown, 3.0 mm long in the fifth instar.
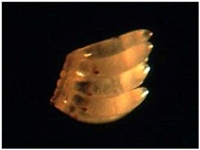
- Adult :
Adult hopper is 4.5-5.0 mm long and has a yellowish brown to dark brown body. The wings are sub hyaline
with a dull yellowish tint. It has two characteristic wing morphs: macropterous (long winged) and brachypterous
(short winged). |
 |
 |
Egg |
Nymph |
 |
 |
Adult |
Adult |
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies: |
|
Cultural Methods:
- Draining the rice field for 3-4 days is recommended during the early stage of infestation.
- Nitrogen application can be split to reduce Brown plant hopper buildup.
- Synchronous planting within 3 weeks of staggering and maintaining a free-rice period could also decrease the build-up of Brown plant hopper.
- There are varieties released by IRRI, which contain genes for Brown plant hopper resistance, like IR26, IR64, IR36, IR56, and IR72.
- Use resistant varieties like PY 3, CO 42, ADT 35, ADT 37, PTB 33 and PTB 21, Aruna, Kanaka, Karthika, Krishnaveni, Makon, Abhey, Asha, Divya.
- Avoid close planting and provide 30 cm rogue spacing at every 2.5 to 3.0 m to reduce the pest incidence.
|
 |
 |
Avoid excess use of
nitrogen |
Intermittent draining of water |
 |
 |
| Provide rogue spacing of 30 cm |
Use resistant variety IR 36 |
|
Chemical Methods:
- ETL : 2 / tiller when 1 spider / hill is present (or) 1 / tiller when spiders are not present (or) 1 hopper/ tiller in the absence of predatory spider and 2 hoppers /tiller when spider is present at 1/hill.
- Drain the water before use of insecticides and direct the spray towards the base of the plants.
- Avoid use of insecticides causing resurgence such as synthetic pyrethroids, methyl parathuion, fenthion and quinalphos.
- Spray any one of the following:
Phosphamidon 40 SL 1000 ml/ha (or) Phosalone 35 EC 1500 ml/ha (or) Carbaryl 10 D 25 kg/ha (or) Methyl demeton 25 EC 1000 ml/ha (or) Acephate 75 SP 625 gm/ha (or) Chlorpyriphos 20 EC 1250 ml/ha Carbofuran 3 G 17.5 kg/ha (or) Dichlorvos 76 WSC 350 ml/ ha.
- Use of botanical methods : Neem oil 3% 15 lit/ha (or) Iluppai oil 6% 30 lit/ha (or) Neem seed kernel extract 5% 25 kg/ha
|
 |
 |
| Spray Chlorpyriphos |
Spray Phosphomidon |
 |
 |
| Spray Acephate |
Use Illupai oil |
|
Biological Methods:
- Release of natural enemies like Lycosa pseudoannulata, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis adult (200 – 250 bugs/ha) during the peak incidence of brown plant hopper at 10 days interval.
- The common parasites of the eggs are the hymenopteran wasps. Eggs are preyed upon by mirid bugs and phytoseiid mites. Both eggs and nymphs are preyed upon by mirid bugs. Nymphs and adults are eaten by general predators, particularly spiders and coccinellid beetles.
- Hydrophilid and dytiscid beetles, dragonflies, damselflies, and bugs such as nepid, microveliid, and mesoveliid eat adults and nymphs that fall onto the water surface.
- Fungal pathogens also infect brown plant hoppers.
|
 |
 |
| Eggs are preyed by phytoseiid mites |
Natural enemy - lycosa pseudoannulata |
 |
 |
| Natural enemy-cyrtorhinus lividipennis |
Predator - Coccinellid beetle |
|
Trap Methods:
- Set up light traps during night.
- Use yellow pan traps during day time.
- Care should be taken not to place light traps near seed beds or fields.
- Installation of light traps with incandescent light at 1-2 m height @ 4/ acre to monitor the population.
- At the base of light trap put a tub filled with water to which kerosene was added to kill the trapped insects.
|
 |
 |
| Incandescent light trap |
Setup light traps |
 |
 |
| Use light trap during night time |
Use yellow pan trap during day time |
| Top |
|
























