|
SEED PRIMING
What is?
Seed priming is the process of controlled hydration of seeds to a level that permits pre-germinative metabolic activity to proceed, but prevents actual emergence of the radicle.
Types of priming
- Hydro priming (use of water double the volume of seed)
- Halo priming (use of salt solution-NaCl)
- Osmo priming (use of osmotic solution – PEG)
- Sand matric priming – (use of moist sand)
Methodology
For the first three methods soak the seed in the respective solution of definite concentration for needed duration and dry back the seed to original moisture content.
For the fourth method mix the seeds with moist sand of required water holding capacity, place it in perforated plastic covers and keep it deep in the tray filled with moist sand of same water holding capacity.
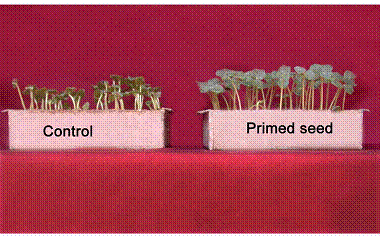
Comparison of control and primed bhendi seeds
Creation of different WHC (Water Holding Capacity)
30% WHC – 90ml of water / kg of dry sand
40% WHC – 120 ml of water / kg of dry seed
60% WHC – 180 ml of water / kg of dry seed
80% WHC – 240 ml of water / kg of dry seed
100% WHC – 300 ml of water / kg of dry seed
| Crop |
Seed priming techniques |
| Tomato |
Hydro priming (48hrs) |
| Brinjal |
Sand matric 80% (3 days) |
| Chillies |
Sand matric 80% (3 days) |
| Onion |
Sand matric 80% (3 days) |
| Carrot |
Hydro priming (36hrs) |
| Beetroot |
Hydro priming (12hrs) |
| Bhendi |
Sand matric60% (3hrs) |
| Radish |
Hydro priming (12hrs) |
| Mustard |
Hydro priming (12hrs) |
Advantages
- Enhances the germination percentage
- Enhances the speed and uniformity of germination
- Improves the resistance towards water and temperature stress
- Increases the shelf life of seed
- Highly suitable for small seeds
- Enhances the yield
For Information
Professor and Head,
Department of Seed Science and Technology,
TNAU, Coimbatore-641 003.
Phone No: Phone: 0422-6611363.
E-mail: seedunit@tnau.ac.in
Updated : Dec, 2014 |

