|
 Blast :Pyricularia grisea (P.oryzae) Blast :Pyricularia grisea (P.oryzae)
| Occurance |
-
Earliest known plant disease
-
Also known as rotten neck or rice fever.
-
Reported from 80 rice-growing countries. First recorded in India during 1918.
-
Expected grain loss : 70 to 80%
|
| Symptom of damage |
|
-
Disease can infect paddy at all growth stages and all aerial parts of plant (Leaf, neck and node).
-
Among the three leaves and neck infections are more severe.
-
Small specks originate on leaves - subsequently enlarge into spindle shaped spots(0.5 to 1.5cm length, 0.3 to 0.5cm width) with ashy center.
-
Several spots coalesce -> big irregular patches
|
| Blast |
Leaf Blast :
Neck Blast
Nodal Blast: Nodes become black and break up
|
| Identification of Pathogen |
Life Cycle of Pyricularia Oryzae |
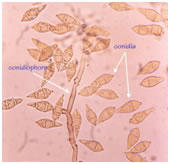 |
| Conidia of Pyricularia Oryzae |
|
|
| Nursery stage |
Light infection - Spray Carbendazim |
| Pre-Tillering to Mid-Tillering |
Light at 2 to 5 % disease severities - Apply Carbendazim @ 0.1 %. Delay top dressing of N fertilizers when infection is seen. Panicle
initiation to booting
At 2 to 5% leaf area damage spray Carbendazim or Tricyclazole @ 0.1 %.
|
| Flowering and after |
At 5 % leaf area damage or 1 to 2 % neck infection spray Carbendazim or Tricyclazole @ 1 g /lit of water.
|
Top
 Bacterial Leaf Blight: Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Bacterial Leaf Blight: Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae
| Symptom of Damage |
- Seedling wilt or kresek
- Water-soaked to yellowish stripes on leaf blades or starting at leaf tips then later increase in lengthand width with a wavy margin
- Appearance of bacterial ooze that looks like a milky or opaque dewdrop on young lesions early in the morning
- Lessions turn yellow to white as the disease advances
- If the cuts end of leaf is kept in water it becomes turbid because of bacterial ooze
|
Healthy Leaf
|
Infected Leaf |
|
| Identification of Pathogen |
Life Cycle of Xanthomonas oryzae |
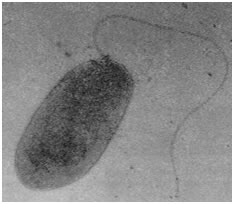 |
| Xanthomonas oryzae |
|
|
| Management |
Biological Method
- Spray fresh cowdung extract 20% twice (starting from initial appearance of the disease and another at fortnightly interval)
- Neem oil 60 EC 3% (or) NSKE 5% is recommended for the control of sheath rot, sheath blight, grain discolouration and bacterial blight
|
Top
 Rice tungro disease : Rice tungro virus (RTSV, RTBV) Rice tungro disease : Rice tungro virus (RTSV, RTBV)
| Symptom of Damage |
-
Plants affected by tungro exhibit stunting and reduced tillering. Their leaves become yellow or orange-yellow, may also have rust-colored spots.
-
Discoloration begins from leaf tip and extends down to the blade or the lower leaf portion
-
Delayed flowering, - panicles small and not completely exerted
-
Most panicles sterile or partially filled grains
|
Healthy Leaf |
Infected Leaf |
|
|
| Management |
Physical Method
- Light traps are to be set up to attract and control the leaf hopper vectors as well as to monitor the population.
- In the early morning, the population of leafhopper alighting near the light trap should be killed by spraying/dusting the insecticides. This should be practiced every day.
- Spray Two rounds of any one of the following insecticides
- Thiamethoxam 25 WDG 100g/ha
- Imidacloprid 17.8 SL 100ml/ha
at 15 and 30 days after transplanting. The vegetation on the bunds should also be sprayed with the insecticides.
- Special detection technique
PCR detection facilities available at the Department of Plant Pathology, TNAU, Coimbatore-3 can be used
|
Top
Main Field Diseases
 Sheath Blight: Rhizoctonia solani Sheath Blight: Rhizoctonia solani
| Symptom of Damage |
Infected sheath
 |
Healthy leaf
 |
Infected leaves
 |
|
-
Plants affected by tungro exhibit stunting and reduced tillering. Their leaves become yellow or orange-yellow, may also have rust-colored spots.
-
Discoloration begins from leaf tip and extends down to the blade or the lower leaf portion
-
Delayed flowering, - panicles small and not completely exerted
-
Most panicles sterile or partially filled grains
|
| Identification of Pathogen |
Life Cycle of Rhizoctonia solani |
 |
 |
| Conidia of Rhizoctonia solani |
|
|
| Management |
Cultural Method
- Apply Neem cake at 150 kg/ha
Botanical
- Foliar spray with Neem oil at 3% (15 lit /ha) starting from disease appearance
|
 |
 |
| Apply Organic Amendments |
Deep Summer Ploughing |
|
Chemicial Method
- Carbendazim 50 WP @ 500g/ha
- Azoxystrobin @ 500ml/ha
- Hexaconazole 75% WG @ 100mg/ lit 1st spray at the time of disease appearance and 2nd spray 15 days later
|
 |
 |
| Spray Iprodione |
Use Polyoxin Antibiotic |
|
Biological control
- Seed Treatment with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation @ 10 ml/kg of seeds
- Seedling root dipping with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation (500 ml for one hectare seedlings)
- Soil application with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation (500ml/ha)
- Foliar spray with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation @ 5ml/lit
|
Top
 Sheath Rot: Sarocladium oryzae Sheath Rot: Sarocladium oryzae
| Symptom of Damage |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Irregular Spots on Sheaths |
Discoloration of Leaf Sheath |
Panicles remain within the Sheath |
Rottening of Flag Leaf Sheath |
|
-
Irregular spots or lesions, with dark reddish brown margins and gray center
-
Discoloration in the flag leaf sheath
-
Lesions enlarge and often coalesce and may cover the entire leaf sheath
-
Severe infection causes entire or parts of young panicles to remain within the sheath
-
Unemerged panicles rot and florets turn red-brown to dark brown
-
Whitish powdery growth inside the affected sheaths and young panicles
-
Infected panicles sterile, shrivelled, or with partially filled grain.
|
| Management |
Cultural Method
- Apply Gypsum @ 500 kg/ha at two equal splits once basally and another at active tillering stage.
- Botanicals
- Neem oil 3%
- Ipomoea leaf powder extract (25 kg/ha)
- Prosopis leaf powder extract (25 kg/ha). First spray at boot leaf stage and second 15 days later
|
 |
 |
| Provide Optimum Plant Spacing |
Apply Potash at Tillering Stage |
|
Chemical Method
- Spray any one of the following:
- Carbendazim @ 500g/ha
- Metominostrobin @ 500 ml/ha
- Hexaconazole 75% WG @ 100 mg/ lit 1st spray at the time of disease appearance and 2nd spray 15 days later
|
 |
 |
| Spray Benomyl |
Spray Chlorothalonil |
|
Biological control
- Seed Treatment with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation @ 10 ml/kg of seeds
- Seedling root dipping with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation (500 ml for one hectare seedlings)
- Soil application with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation (500ml/ha)
- Foliar spray with TNAU Pf 1liquid formulation @ 5ml/lit
|
Top
 Brown Spot : Helminthosporium oryzae Brown Spot : Helminthosporium oryzae
| Occurance |
Also called as sesame leaf spot or Helminthosporiose or fungal blight
Mostly seen in West Bengal, Orissa, A.P and Tamil Nadu
|
| Occurance |
-
Occur in nursery as well as main field
-
Causes blight of seedlings
-
Leaf spotting is very common
-
Isolated brown, round to oval (resemble sesame seed)
-
Spots measures 0.5 to 2.0mm in breadth - coalesce to form large patches.
-
Seed also infected (black or brown spots on glumes spots are covered by olivaceous velvety growth)
-
Infection also occurs on panicle neck with brown colour appearance
-
50% yield reduction in severe cases
|
Healthy field
 |
Infected leaf
 |
Advanced stage of infection
 |
|
| Occurance |
-
Also called as sesame leaf spot or Helminthosporiose or fungal blight
-
Mostly seen in West Bengal, Orissa, A.P and Tamil Nadu
|
| Symptoms |
-
Occur in nursery as well as main field
-
Causes blight of seedlings
-
Leaf spotting is very common
-
Isolated brown, round to oval (resemble sesame seed)
-
Spots measures 0.5 to 2.0mm in breadth - coalesce to form large patches.
-
Seed also infected (black or brown spots on glumes spots are covered by olivaceous velvety growth)
-
Infection also occurs on panicle neck with brown colour appearance
-
50% yield reduction in severe cases
|
|
| Identification of Pathogen |
Life Cycle of Helminthosporium oryzae |
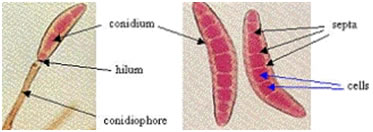 |
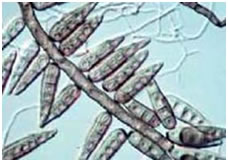 |
| Conidia of Helminthosporium oryzae |
|
|
| Management |
Spray any one of the following:
- Metominostrobin @ 500ml/ha
|
Top
 False Smut: Ustilaginoidea virens False Smut: Ustilaginoidea virens
| Symptoms |
-
Only few grains in a panicle are usually infected and the rest are normal
-
Individual rice grain transformed into a mass of yellow fruiting bodies
-
Growth of velvety spores that enclose floral parts
-
Immature spores slightly flattened, smooth, yellow, and covered by a membrane
-
Growth of spores result to broken membrane
-
Mature spores orange and turn yellowish green or greenish black
|
Healthy grain
 |
Infected panicle
 |
Infected grain
 |
|
| Identification of Pathogen |
 |
 |
| Conidia of Ustilaginoidea virens |
|
|
| Management |
- Two sprayings of Propiconazole 25 EC @ 500ml/ha (or) Copper hydroxide 77 WP @ 1.25 kg/ha at boot leaf and 50% flowering stages
|
Top
 Grain discoluration – fungal complex Grain discoluration – fungal complex
| Symptoms |
- Drechslera oryzae, Curvularia lunata, Sarocladium oryzae, Phoma sp., Microdochium sp., Nigrosporasp. and Fusarium sp.,
- Grains are infected either after milk stage or after harvest or during storage
- Infection may be internal or external causing discoluration of the glumes or kernels
- Dark brown or black spots appear on grains
- Under humid condition prominent fungal growth
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Discolouration of grains |
Black Spots Appear on
Grains with Prominent
Fungal Discolouration |
Black Spots Appear on
Grains |
Fungal Growth on Grains |
|
| Management |
Chemical Method
- Spray - Carbendazim + Thiram + Mancozeb (1:1:1) 0.2% at 50% flowering stage.
|
 |
| Spray Mancozeb at Boot Leaf Stage |
|
Top
 Leaf streak -Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola Leaf streak -Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola
| Symptom |
-
Initially, small, dark-green, water-soaked translucent streaks on veins from tillering to booting stage
-
Lesions turn brown and bacteria ooze out under humid weather.
|
 |
 |
Brown to Greyish
Longitudinal Streaks on
Leaves |
Lesions turn brown to greyish and drying of leaves |
|
| Management |
Biological method
- Spray fresh cowdung water extract 20%
- Copper hydroxide 77 WP@1.25 kg/ha is also recommended
|
 |
Spray Cowdung or Mint or
Lemongrass Extract |
|
Updated on May, 2014 |

